I’ve produced a pilot episode of a “Probability Podcast”. Please have a listen and let me know if you’d be interested in hearing more episodes. Thanks!
The different approaches of Fermat and Pascal
Pascal’s solution, which may have come first (we don’t have all of the letters between Pascal and Fermat, and the order of the letters we do have is the matter of some debate), is to start at a point where the score is even and the next point wins, then work backwards solving a series of recursive equations. To find the split at any score, you would first note that if, at a score of (x,x), the next point for either player results in a win, then the pot at (x,x) would be split evenly. The pot split for player A at (x-1,x) would be the chance of his winning the next game, times the pot amount due him at (x,x). Once you know the split in the case where player A (or B) lacks a point, you can then solve for the case where a player is down by two and so on.
Fermat took a combinatorial approach. Suppose that the winner is the first person to score N points, and that Player A has a points and Player B has b points when the game is stopped. Fermat first noted that the maximum number of games left to be played was 2N-a-b-1 (supposing both players brought their score up to N-1, and then a final game was played to determine the winner). Then Fermat calculated the number of distinct ways these 2N-a-b-1 might play out, and which ones resulted in a victory for player A or player B. Each of these combinations being equally likely, the pot should be split in proportion to the number of combinations favoring a player, divided by the total number of combinations.
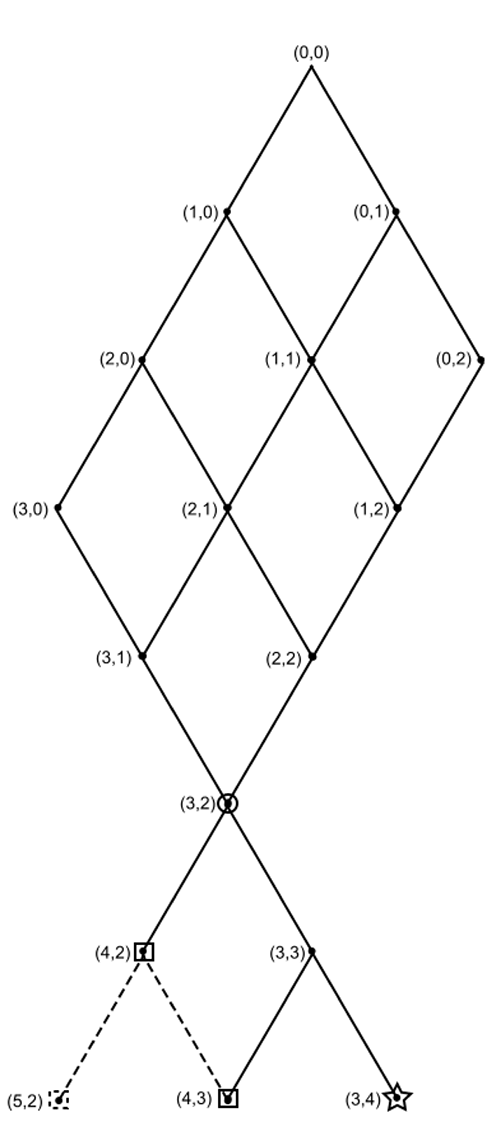
To understand the two approaches to solving the problem of points I have created the diagram shown at right.
Suppose each number in parenthesis represents the score of players A and B, respectively. The current score, 3 to 2, is circled. The first person to score 4 points wins. All of the paths that could have led to the current score are shown above the point (3,2). If player A wins the next point then the game is over. If player B wins, either player can win the game by winning the next point. Squares represent games won by player A, the star means that player B would win. The dashed lines are paths that make up combinations in Fermat’s solution, even though these points would not be played out.
Pascal’s solution for the pot distribution at (3,2) would be to note that if the score were tied (3,3), then we would split the pot evenly. However, since we are at point (3,2), there is only a one-in-two chance that we will reach point (3,3), at which point there is a one-in-two chance that player A will win the game. Therefore the proportion of the pot that goes to player A is 1/2+1/2 (1/2)=3/4 whereas player B is due 1/2 (1/2)=1/4.
Fermat’s approach would be to note that there are a total of 4 paths that lead from point (3,2) to the level where a total of 7 points have been played:
(3,2)→(4,2)→(5,2)
(3,2)→(4,2)→(4,3)
(3,2)→(3,3)→(4,3)
(3,2)→(3,3)→(3,4)
Of these, 3 represent victories for player A and 1 is a victory for player B. Therefore player A should get 3/4 of the pot and player B gets 1/4 of the pot.
As you can see, both Pascal and Fermat’s solutions yield the same split. This is true for any starting point. Fermat’s approach is generally agreed to be superior, as the recursive equations of Pascal can become very complicated. By contrast, Fermat’s combinatorial method can be solved quickly using what we now call Pascal’s Triangle or its related equations. However, both approaches are important for the development of probability theory.


